A data processor handles personal data for a controller, following instructions and GDPR rules to ensure security, compliance, and privacy.
The data processor processes personal data only on behalf of the controller. The data processor is usually a third party external to the company. However, in the case of groups of undertakings, one undertaking may act as processor for another undertaking.
What Is a Data Processor:
A data processor is an individual or organization that processes personal data on behalf of a data controller. The term is defined by data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the UK GDPR. The data processor’s role is crucial in handling personal data, but they do so under the direction and authority of the data controller, who determines the purpose and means of the data processing.
What Duties Do Data Processors Have:

Data processors have specific duties and responsibilities under data protection laws. These duties include:
- Processing data only on documented instructions from the data controller.
- Implementing technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of data.
- Assisting the data controller in ensuring compliance with data protection obligations, such as managing data breaches and conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs).
- Maintaining records of all data processing activities they carry out on behalf of the data controller.
- Not engaging another processor without prior authorization from the data controller.
- Deleting or returning all personal data to the data controller after the end of the provision of services.
What Does Data Processor Mean:
The term data processor specifically refers to an entity that processes personal data on behalf of another entity (the data controller). The processor’s role does not include determining the purposes or means of the processing; instead, it is tasked with following the controller’s instructions. Examples of activities carried out by data processors include storing, organizing, retrieving, and securing personal data.
Examples of Data Processors:
Data processors can be a variety of organizations or individuals, including:
- Cloud storage providers who store personal data for businesses.
- Email marketing companies that send communications to customers on behalf of businesses.
- Payroll service providers that process employee salary data.
- Analytics companies that process data to provide insights and reports for other businesses.
What Is a Sub-Processor:
A sub-processor is a third party engaged by a data processor to assist with processing personal data on behalf of a data controller. The use of sub-processors must be pre-approved by the data controller, and the sub-processor must adhere to the same data protection obligations as the primary data processor. Both the processor and sub-processor must have written agreements outlining their responsibilities and adherence to GDPR requirements.
GDPR Compliance and Data Processors:
Under the GDPR, data processors must comply with specific legal requirements to ensure the security and lawful processing of personal data. Key compliance requirements include:
- Processing data according to the GDPR principles (lawfulness, fairness, transparency, accuracy, and minimization).
- Implementing appropriate security measures to protect data against unauthorized or unlawful processing.
- Notifying the data controller of any data breaches without undue delay.
- Conducting regular audits and assessments to ensure ongoing compliance with GDPR.
Data Processor Personal Responsibilities:
Data processors are personally responsible for:
- Ensuring they follow all instructions provided by the data controller.
- Implementing adequate data protection measures.
- Reporting data breaches promptly to the data controller.
- Maintaining accurate records of all data processing activities.
Data processors may face legal consequences, including fines and penalties, if they fail to comply with GDPR requirements.
Are You a Data Processor:
If you handle personal data solely on behalf of another entity and follow their specific instructions, you are likely considered a data processor. Common examples include IT service providers, outsourced HR firms, and marketing agencies that manage data for other businesses.
Data Processing Obligations – Critical GDPR Articles:
Several GDPR articles outline the obligations of data processors:
- Article 28: Sets out requirements for data processor contracts.
- Article 30: Requires data processors to maintain records of all processing activities.
- Article 32: Mandates appropriate technical and organizational security measures.
- Article 33: Requires data processors to notify data controllers of any personal data breaches without undue delay.
Also read: Socket 1366 Processor List – An Extensive Guide!
Who Does the UK GDPR Apply To:
The UK GDPR applies to:
- Data controllers and processors operating within the UK.
- Organizations outside the UK that offer goods or services to individuals in the UK or monitor their behavior.
Both data controllers and processors must ensure compliance with the UK GDPR when handling personal data.
Your Business and Your Data Protection System:
Businesses must establish a robust data protection system that includes:
- Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if required.
- Ensuring contracts with processors meet GDPR requirements.
- Implementing data protection policies and training for employees.
- Regularly reviewing and updating security measures to protect personal data.
Are Employees Classed As Data Processors:
Employees are not generally considered data processors under GDPR. However, if an employee processes personal data on behalf of their employer, they may carry out the role of a data processor within the organization. Employees must follow their employer’s data protection policies and the instructions of the data controller.
An Example and Tasks Of A Data Processor:
A payroll company is an example of a data processor. The company processes employee data, such as names, addresses, salaries, and bank details, solely based on the instructions of its client (the data controller). The tasks of the data processor in this context include securely handling, storing, and transmitting payroll data.
Personal Data Processing, Record Keeping, and Secure Processing Architecture:
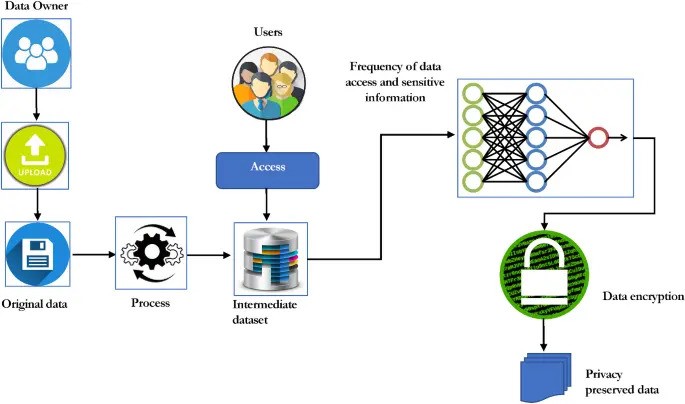
Data processors must ensure that personal data is processed securely, maintain records of processing activities, and establish a secure processing architecture that includes:
- Data encryption and anonymization to protect sensitive information.
- Access controls to restrict unauthorized access to data.
- Regular audits and risk assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Backup and recovery plans to safeguard data against loss or damage.
FAQ’s:
1. What is a data processor?
A data processor is an entity or individual that processes personal data on behalf of a data controller, following their instructions.
2. What are the responsibilities of a data processor?
Data processors must ensure data security, follow the controller’s instructions, maintain records, and report data breaches.
3. What is a sub-processor?
A sub-processor is a third party engaged by a data processor to help with data processing tasks on behalf of the data controller.
4. How does GDPR apply to data processors?
GDPR requires data processors to comply with specific obligations, including data security measures, breach notifications, and maintaining processing records.
5. Are employees considered data processors?
Employees are not generally considered data processors; however, they may act as data processors within their organization, following internal data protection policies.
Conclusion:
Data processors play a critical role in managing personal data on behalf of data controllers while adhering to strict GDPR regulations. Their responsibilities include implementing robust security measures, maintaining accurate records, and ensuring compliance with data protection laws. Understanding the duties and obligations of data processors is essential for businesses to protect personal data effectively.